Bank Statement Analysis: Why is it Vital for Businesses with Multiple Accounts?

Bank statement analysis is important in obtaining and analysing financial data for finance and corporate management. According to Shopify, financial statements serve as an accounting form of assessing a business’s health. Although having a single bank statement for a business can provide valuable insights, but it becomes increasingly challenging once the business has multiple accounts.
In this scenario, aggregate bank statement analysis can be helpful to get a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health.
This blog will explore how automated bank statement analysers can assist in speeding up the process of analysing aggregate bank statements for different accounts within the same firm.
What is Account Aggregation?
Before getting into the technicalities of aggregate bank statement analysis, it is critical to understand what the term “aggregation” means in the context of financial data. It is the process of integrating and incorporating financial information from many sources or accounts in order to offer a consistent and strong picture of a company’s financial situation.
On the other hand, account aggregation is the process of combining financial data from several sources into a single overview. In the context of bank statement analysis, account aggregation involves collecting and aggregating financial data from numerous bank accounts held by a single business organisation.
Consider a retail chain with multiple locations, each with its own bank account. In addition, the company has a corporate account and a savings account. The account aggregation process gathers financial transaction data from all of these accounts and presenting it to the analyst as a unified financial overview.
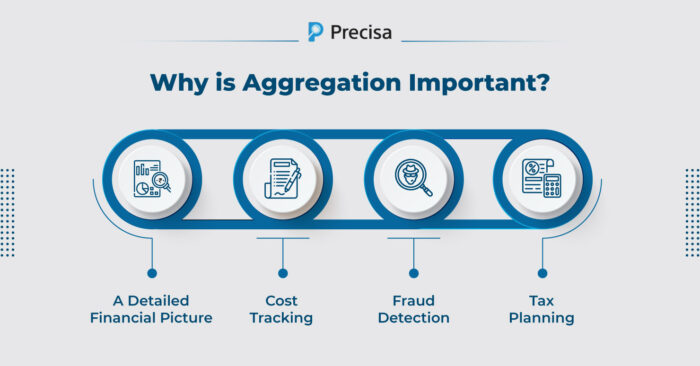
Why is Aggregation Important?
When a company has many accounts for varied purposes, such as operating expenses, payroll, savings, and investments, aggregating bank data becomes critical.
Here are a few reasons why aggregation is critical:
-
A Detailed Financial Picture
Individual bank statements cannot be used to evaluate a company’s financial condition precisely. By combining all financial data, aggregation allows decision-makers to see the larger picture. This birds-eye perspective helps make informed financial decisions and analyse the organisation’s overall performance.
-
Cost Tracking
Businesses frequently have several accounts set up for various purposes. Aggregating statements allow for proper cost tracking across these accounts. This is particularly important for budgeting and cost control, ensuring no expenses are missed.
-
Fraud Detection
Aggregation can more efficiently identify errors or variations in financial transactions. Consolidating data from multiple accounts makes it easier to identify unusual activity or potential fraud within the organisation.
-
Tax Planning
Having all financial data aggregated simplifies the procedure and decreases the chance of errors when completing tax returns. This assures tax compliance and reduces the risk of audits.
Bank Statement Analysis for Multiple Accounts: Some Challenges?
While the advantages of account aggregation are evident, adopting and executing aggregated bank statement analysis for several accounts within the same company can be difficult. Several challenges must be overcome in this process:
1. Data Safety
Handling sensitive financial data from various accounts requires strict safety measures to prevent data breaches and unauthorised access. This adds an additional layer of complication to the evaluation of aggregated bank statements.
2. Volume of Data
Managing and analysing data from multiple accounts can be overwhelming and may require more sophisticated software or expertise.
3. Time-Consuming Process:
The evaluation can be tedious, especially if manual intervention is required to sort or categorise certain transactions.
4. Detection of Fraudulent Activities:
With multiple accounts, keeping track of suspicious activities becomes more intricate.
How Automated Bank Statement Analyzers Simplify Aggregation
An automated statement analyser tool can help in aggregating bank statement analysis for multiple accounts within the same business. It typically involves several key steps:
1. Data Collection
- Data Sources: The automated analyser is configured to connect to various data sources, which may include different bank accounts, credit card accounts, financial institutions, and other financial data repositories. It uses secure connections, such as APIs or secure file transfers, to access account information.
- Data Retrieval: The software retrieves transaction data, including deposits, withdrawals, transfers, and other financial activities, from each connected account.
2. Data Integration
- Data Mapping: The bank statement analysis software maps the data from different accounts to a standardised format, ensuring consistency in terminology and structure. This mapping is crucial for combining data from various sources into a unified view.
- Data Transformation: Any necessary data transformations or conversions are performed to ensure that data from different sources can be effectively aggregated and analysed together.
3. Data Consolidation
The automated analyser employs algorithms to consolidate data from multiple accounts. It reconciles transactions, eliminating duplicates and ensuring that the consolidated data accurately reflects the business’s financial activities.
4. Real-Time Updates
Many automated analysers offer real-time or scheduled data synchronisation with connected accounts. As new transactions occur in any of the accounts, the system updates the consolidated financial view immediately or at predefined intervals.
6. Reporting and Analysis
- Custom Reporting: Users can generate customised reports and dashboards that provide a comprehensive view of the financial status across multiple accounts. These reports can be tailored to meet specific business requirements.
- Analysis Tools: Automated analysers often include analytical tools that allow users to identify trends, anomalies, key performance indicators (KPIs), and other insights from the consolidated financial data.
7. Compliance and Audit Trail
- Compliance Features: The software may include features to assist with regulatory compliance, such as generating compliance reports or documenting financial transactions in accordance with industry standards.
- Audit Trail: An audit trail is maintained to track changes and activities related to financial data, providing a transparent record for auditing purposes.
Therefore, a modern bank statement analyser allows businesses to analyse multiple accounts in a unified and accessible manner by collecting diverse information, thereby increasing the accuracy and usability of financial information.
Summing Up!
Managing multiple accounts can make it difficult to maintain accurate oversight in today’s complex financial landscape. Aggregate bank statement analysis offers a solution, consolidating data from various accounts. While beneficial, it also poses security data and integration challenges.
Fortunately, automated bank statement analysers address these issues, simplifying data aggregation, enhancing security, and providing real-time updates.
With secure, paperless, real-time sharing, Precisa’s automated bank statement analyser makes multi-account data aggregation easier. Requiring only a single consent to access data reduces the risk of fraud and conveniently connects with Account Aggregator services.
Users have quick upload and fetch capabilities to ensure accurate analysis of various accounts. Additionally, Precisa allows users to export this analysed data to Excel for further processing and reporting, making it a versatile and efficient tool for financial management.
Book a free trial to learn more about Precisa!