Future Outlook: The Evolving Relationship Between Fintech and Banks

Fintech combines finance and technology; it is transforming the financial landscape and reshaping the future of finance, leading to a collaboration between fintech and banks. Generally, it refers to businesses that leverage technology to improve and automate their financial services and processes.
Fintech encompasses a rapidly growing trend, making financial services inclusive and efficient and promoting economic development benefiting consumers and businesses in numerous ways.
As per Expert Market Research reports, the global fintech market stood at approximately USD 194.1 billion in 2022; expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.8%, the market size will reach USD 492.81 billion by 2028.
Initially, fintech companies were viewed as disruptors and challengers to the traditional banking industry. This view has given way to banks embracing fintech, and both sectors are collaborating increasingly.
This blog post explores the evolving relationship between fintech and banks and evaluates the future outlook.
Fintech and Banks: An Evolving Relationship
The financial industry is witnessing a transformation owing to the combined impact of factors like changing customer expectations, technological innovations and reforms in the regulatory framework.
However, evolving financial technology may be regarded as a double-edged sword for the banking sector. On the one hand, it may pitch fintech and banks as competitors, vying for the loyalty and attention of the same customers in this fast-evolving market; on the other hand, it can help banks enhance customer experience and improve efficiency by using tools like a chatbot or employ machine learning to prevent fraud.
Considering fintech and banks as merely competitors gives a simplistic view of the evolving dynamics. Fintechs can help businesses customise and personalise their services and products and diversify their offerings. Service providers need to analyse and convert customer data into actionable insights to offer customised solutions; this is made possible by employing technology.
Traditional banks and fintech companies realise that a seamless model that combines the strengths of each benefit both parties and allows them to offer innovative solutions to customers. For example, co-lending is one such model that combines the strengths of fintech and banks; it offers a win-win for all parties and is fuelling India’s growth.
Factors Driving the Collaboration Between Banks and Fintech
Below is a look at 5 key factors that promote collaboration between fintech and banks.
1. Innovative Technology
Fintech companies have the advantage of innovative technology when compared to traditional banks. This helps them develop innovative products and services that appeal to consumers. Examples of employing innovative technology include mobile banking apps that allow customers to have a real-time view of their accounts.
Such products offer convenience, are user friendly and more affordable compared to the offerings from traditional banks.
2. Improved Efficiency
Fintech companies are helping banks improve their operational efficiency with the help of technology. Automating tasks using artificial intelligence and machine learning reduces the chances of fraud, improves and hastens the onboarding process and provides enhanced customer service. This helps banks reduce costs, retain customers and reduce the turnaround time.
3. Support From Regulators
Regulators are also actively offering support for fintech innovation and research. They are offering regulatory sandboxes where fintech companies can test new products and services without the need to meet all the regulations that apply to traditional banks. Sandboxes are helping create a more level playing field for fintech companies and banks while at the same time encouraging innovation.
4. Wider Market Share
Collaboration between fintech and banks allows both stakeholders to tap into the customer base of the other, helping them increase their market share and aiding financial inclusion.
Fintech companies would benefit from the well-defined and stable customer base banks have. The coming together of fintech and banks has resulted in solutions like Open Banking that have democratised data and made them collaborate and harness the power of raw data.
5. Symbiotic Relationship
Banks are data-rich owing to their long-standing presence and relationship with customers; fintech firms are better at leveraging this data to improve their product range and customer experience.
Fintechs must adapt and innovate at a rapid pace to keep up with the changing expectations of customers. This can help banks, which are generally slow to adapt to change due to size and sometimes regulatory issues.
Banks rely on their legacy and customer loyalty, while fintechs count on data to understand customers and shape their relationship with them.
What Does the Future Hold for Fintech and Bank Partnership?
The future of the fintech and banks relationship is one of cooperation and collaboration to create a more efficient and customer-centric financial services industry.
Below are three use cases of this integration
1. BaaS
Fintech partnerships could take the form of BaaS or Banking-as-a-Service relationships. In this case, banks offer services that nonbanks can’t provide themselves due to regulatory guidelines or other reasons.
As per a study, 7% of the survey respondents currently offer BaaS, 13% were actively considering it, and 46% said they might use BaaS in the future; it is one of the fintech trends to look out for in 2023.
The BaaS business model is currently underutilised, which means there is ample opportunity for traditional banks, NBFCs, and fintech firms to collaborate and reach out to this segment with innovative banking products.
2. Growing Trend Of Alliances
A growing number of banks in India are also partnering with fintech companies across verticals to offer co-branded cards, PoS solutions, lending and insurance offerings. This trend of alliances is likely to continue, driving penetration in newer markets and helping meet untapped demands.
Newer banks favour an asset-light model as they explore fintech partnerships that help them widen distribution without investing in large branch networks.
3. Embedded Finance
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable the co-creation of innovative solutions between banks and fintech companies. Embedded banking facilitates seamless integration of banking products in fintech user apps.
Examples are insurance coverage within ridesharing apps or financial management tools built into e-commerce platforms.
The future for embedded finance holds promise as the global embedded finance market is expected to reach $384.8 billion by 2029, growing at a rate of 30%, further strengthening the relationship between fintech and banks.
To Sum It Up
While the future of fintech and banks collaboration holds promise, it comes with the inevitable concerns related to security and privacy due to data sharing.
Keeping sensitive financial data safe is critical for financial institutions and consumers. All stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, are focusing on educating users about the need to build secure financial solutions.
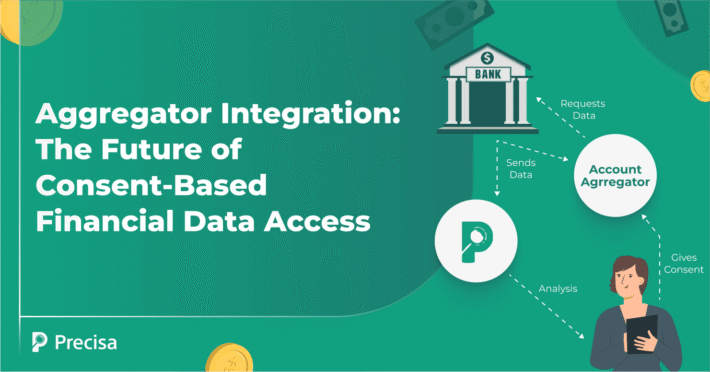
As an AI-enabled, cloud-based fintech platform, Precisa offers multiple solutions, such as Bank Statement Analysis, GSTR Analysis and Account Aggregator Integration, etc., that can be easily integrated with existing processes and systems without compromising data security. These solutions use technology to offer seamless, safe and swift data sharing in real time and help minimise fraud risk.
Book a free trial to learn more about Precisa!