How to Analyse a Credit Card statement
Although India’s credit card market remains underpenetrated compared to some developed economies such as the US and China or developing economies such as Brazil, there is a higher penetration opportunity in India.
According to a 2020 report published on ResearchAndMarkets, the Indian credit card industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of more than 25% during 2020 – 2025. This is due to the popularity of credit cards and the trend of purchasing products first and paying for them later. The number of credit card users in India in 2019 touched 52 million.
With the growth in credit cards, there has also been an increase in credit products, including personal loans, credit card offers, etc. Credit card statements are also used as part of the credit assessment process by lending institutions and banks.
What is a Credit Card Statement?
A credit card statement is a periodic statement that summarises credit card usage for the billing period. The credit card issuer sends a statement about once a month.
Credit card statements are good indicators of an individual’s or a business’s expenses, credit utilisation, debt history and spending patterns. Along with the borrower’s bank statements and credit report, they determine the borrower’s creditworthiness.
The data contained in credit card statements can be used to gain insight into credit patterns. In personal finance cases, this information can be used to plan future spending by the individual or business. In the lending industry, most information regarding credit lines is assessed through credit bureau reports. Still, errors in these reports are not uncommon, and credit card statements can aid in investigating such instances. In addition, credit card statements are a determinant in credit assessment for new cardholders who do not have a long credit history.
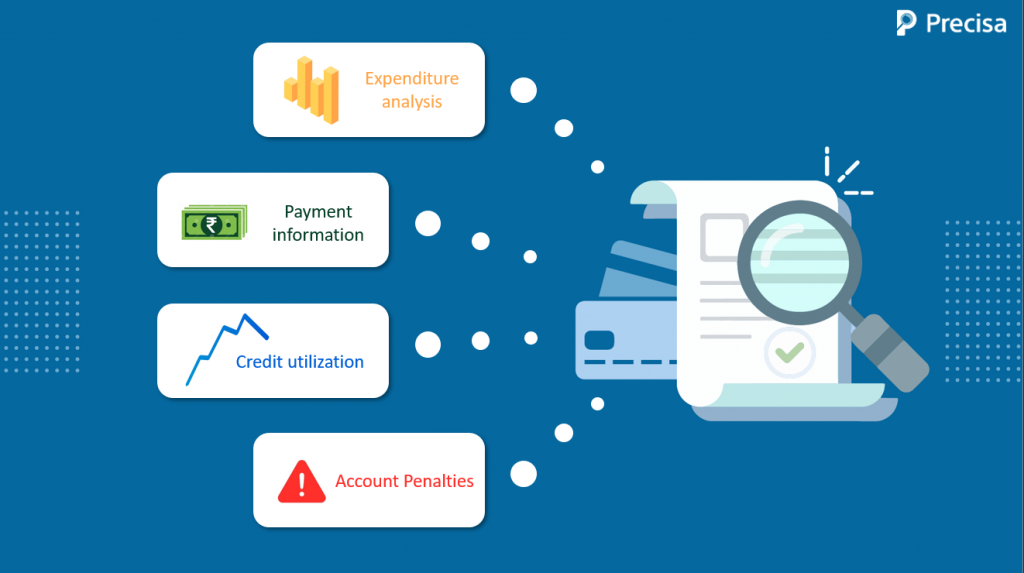
What Insights Can Be Obtained From Credit Card Statements?
A credit card statement generally consists of five sections:
- Account summary – It includes the credit limit, available credit and a high-level breakdown of current balance into outstanding debt, purchases, balance transfers, fees, etc.
- Payment information – The minimum payment due as well as a warning for late payments are displayed.
- Notice of changes to the account terms – This section informs you about important changes to the account, such as an increase in interest due to a late penalty, over utilising the credit limit, etc.
- Transaction history – A record of all transactions since the last statement. In every statement, fees and interest charged over purchases are displayed separately, with a total of fees and interest so far for the current year.
- Interest calculation – A summary of the interest rates charged for each type of transaction, the account balance, the amount of each, and the interest rate charged.
The above credit card statement information can provide a clearer view of what an individual or company’s credit behaviour looks like. The main insights derived from this data include the following:
Payment information
This includes the number and details of late payments if any, and the minimum payment trend across months. In addition, bill payments affect credit since only paying the minimum amount due is not a good indicator of a reliable and responsible borrower.
Among the essential evaluative factors that affect a borrower’s credit history is payment history, including late payments, debts, minimum payments, etc.
Credit utilisation
There is usually a limit on the amount the cardholder can spend on their credit card. The credit card utilisation shows the usage for the credit limit. There also exist credit cards with no limit where the cardholder has to pay the entire amount charged on the card every month.
Credit utilisation is one of the most critical factors that affect the credit report. Lower utilisation is better for credit scores, with anything under 30% being considered good. However, 0% is not the best since having some utilisation is better than none.
Debts and Penalties
Credit cards follow the trend of purchasing first and paying later. Due to this, it is possible to incur debts and penalties if credit card payments are not made on time.
The failure to pay off the credit card balance and transfer it to the next month results in penalties and credit card debt, which negatively impacts a borrower’s credit history. These penalties are largely in the form of higher interest rates on credit cards.
Fraud/Error detection
When analysing credit card statements, it is vital to look for signs of fraud, such as tampering or errors.
This is done by analysing and cross-checking various sections of the credit card statement, like account summary information. And minimum payments due are cross-checked with transactions and previous balance, with year-to-date details compared to prior statements, etc.
Expenditure analysis
Credit card statements contain transaction history for a specified period. Moreover, it provides detailed information on expenditures, transfers, penalties, bill payments, recurring payments, etc.
In addition to this, credit card statements can be analysed with bank statements to get a deeper understanding and insights like the debt-to-income ratio.
How to Perform Credit Card Statement Analysis?
Credit card statement analysis provides insight into the credit behaviour and utilisation of an individual or business based on the history of transactions.
For lending institutions, this data is crucial in scenarios when the borrower is a new entrant in the market and doesn’t have a long credit history or when there’s a need to investigate a possible default on the credit report.
Manually analysing credit card statements presents some challenges –
- Credit Card statements contain a lot of information, including a list of all transactions, making it difficult and time-consuming to analyse them.
- Manually analysing hundreds of pages of statement data increases the risk of human error and subjective biases.
- The content of a credit card statement is not consistent and changes with the issuer, or in some cases, the card type as well.
A more efficient solution is to use an automated credit card statement analyser. Automating the process through Artificial Intelligence (A.I) makes the analysis faster with better and accurate results. There are many benefits to this. The top ones are:
Better resource utilisation
- The amount of time required to analyse a credit card statement is reduced significantly when automated, making credit assessment more time-efficient.
- With the introduction of A.I, the human resources that were involved in manual analysis before can now be deployed elsewhere, thereby decreasing the cost incurred by the institution.
More reliability
With larger and multiple statements, manual analysis becomes tedious and more prone to errors. However, with thoroughly tested software, the parsing and analysis of the same can be completed in much less time and with fewer errors, resulting in a more reliable process.
Parsing hundreds of pages and multiple account statement data manually is daunting, could cause errors or be subjected to biases. By automating the process with Artificial Intelligence, the analysis becomes faster, objective and eliminates human error.
A cost-effective analytical tool, Precisa provides credit card statement analysis and bank statement and GSTR analysis with aggregate analysis to make credit assessment simple, efficient, and convenient. Try Precisa’s 14-day FREE trial.