Why Anti-Money Laundering Analysis is a Must for All Lenders

As lenders scale their businesses, they are more vulnerable to exposure to activities such as money laundering. The estimated value of money laundered globally is 2 to 5% of the global GDP, or $800 billion.
The real figure, however, may be higher. Therefore, lenders who want to protect their businesses from the consequences of money laundering are advised to implement strong safeguards.
In this blog post, we deconstruct anti-money laundering analysis, which is emerging as a best practice in the financial services sector.
What is Anti-Money Laundering Analysis?
Anti-money laundering analysis is a structured approach adopted by lenders to ensure that their operations do not become a channel for criminals to launder money.
Failure to institute a robust anti-money laundering framework can trigger various consequences for lenders:
- They open themselves up to investigation by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other authorised bodies.
- They may face financial consequences such as fines that run into millions.
- Lending operations may be frozen.
- Lending operating licenses may be revoked.
- Reputational loss and potential shutdown may follow.
Today, the full spectrum of lenders—from banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) to digital lenders and payment apps—are susceptible to money laundering activities. The potential for misuse grows as companies attempt to drive revenues and scale their businesses quickly.
Key Anti-Money Laundering Analysis Strategies
Lenders must institute a strong framework to comply with anti-money laundering regulations. Here are the key pillars:
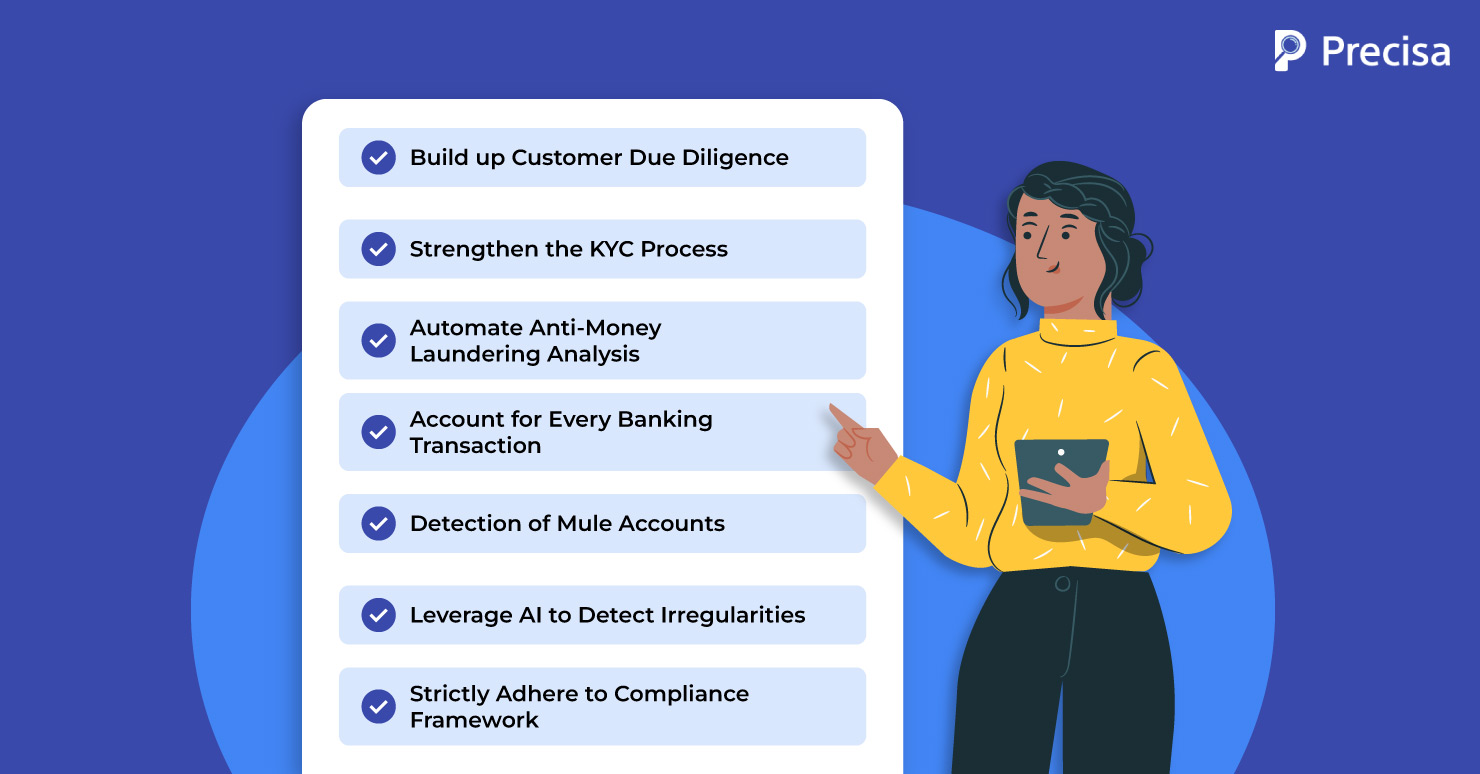
1. Build up Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
As lenders rush to fulfil their revenue targets, they must invest proportional efforts in strengthening Customer Due Diligence (CDD). This denotes the process of verifying multiple aspects related to loan applicants to help establish their authenticity.
Here are examples of key aspects that lenders must look into at the onset:
- A customer’s identity
- A customer’s risk profile
- All business activities
- Bank transaction patterns
- Track cash flow sources, uses and counterparties
- Evaluation of the nature of business relationships
- Ensure transaction consistency
Customer profiles accompanied by higher risk, such as high net worth individuals and Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), must be scrutinised with more caution.
2. Strengthen the KYC Process
For several lending businesses, Know Your Customer (KYC) has become a standardised activity that must be ticked off a checklist. Lenders are required to perform KYC as part of the underwriting process and at regular intervals once a borrower is converted into a customer.
However, lenders must institute foolproof processes to cross-check the authenticity of documents. In this scenario, AI can empower lending teams to be thorough during the KYC process and spot errors that the human eye may miss.
3. Automate Anti-Money Laundering Analysis
Lenders must use automation to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of anti-money laundering protocols. Specialised anti-money laundering analysis software, for instance, can help automate key functions:
- Multi-account analysis can be performed seamlessly and quickly.
- A borrower’s financial data can be automatically pulled from authorised sources.
- The process of authenticating all borrower documents can be fully automated.
- The bank statement analysis process can be automated to ensure that it is comprehensive and conclusive.
Contemporary automation uses a mix of technologies to drive superior results. These comprise:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Cloud computing
- Robotic automation
The use of such advanced technology enables lenders to weed out any potential money laundering schemes.
4. Account for Every Banking Transaction
Lenders can leverage AI-powered anti-money laundering analysis software solutions to ensure that every banking transaction is accounted for.
- The software extracts bank data and automatically segregates every transaction into an inflow or outflow category.
- The inflow and outflow categories are further segregated into over 25 to 30 categories each. Here are some examples:
- Inflow categories comprise revenues, income tax refunds, earned interest, and capital gains.
- Outflow categories comprise employee salaries, vendor payments, customer refunds, EMIs, fees, and fines.
- The software flags any transactions that cannot be categorised clearly, and the lender can investigate such cases.
- Lenders can leverage monthly maximum and minimum balance detection analysis capabilities to understand cash flow patterns.
The software performs a comprehensive analysis and produces an anti-money laundering risk score. Lenders can use this score to make data-driven decisions during the underwriting process.
5. Detection of Mule Accounts
A mule account is a bank account used to launder money. Superior anti-money laundering analysis software includes mule account detection technology, which helps identify mule accounts in a borrower’s banking data.
6. Leverage AI to Detect Irregularities
The adoption of AI can help lenders detect irregularities in borrower data in a number of ways:
- AI can detect irregular banking transaction patterns that are invisible to the human eye.
- It can identify minute differences in documents, which can translate to genuine errors or potential forgery.
- The use of AI makes it challenging for borrowers to commit identity theft, as the technology can identify inconsistencies across large volumes of data.
7. Strictly Adhere to Compliance Framework
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has instituted a comprehensive regulatory framework against money laundering.
By adhering to all the regulatory guidelines, lenders can effectively build a culture of compliance and safeguard their businesses. AI and ML can help lenders automate this process.
Key Takeaway
An effective anti-money laundering program requires a combination of strategy, expertise, human invention, automation, and continuous monitoring.
Lenders that invest early in AI-powered anti-money laundering analysis software will be better equipped to address the problem efficiently, especially as they scale.
Presica’s comprehensive and seamless financial data analysis solution simplifies and speeds up the process through automation. The software provides actionable insights on a customisable dashboard, helping companies make informed business decisions.